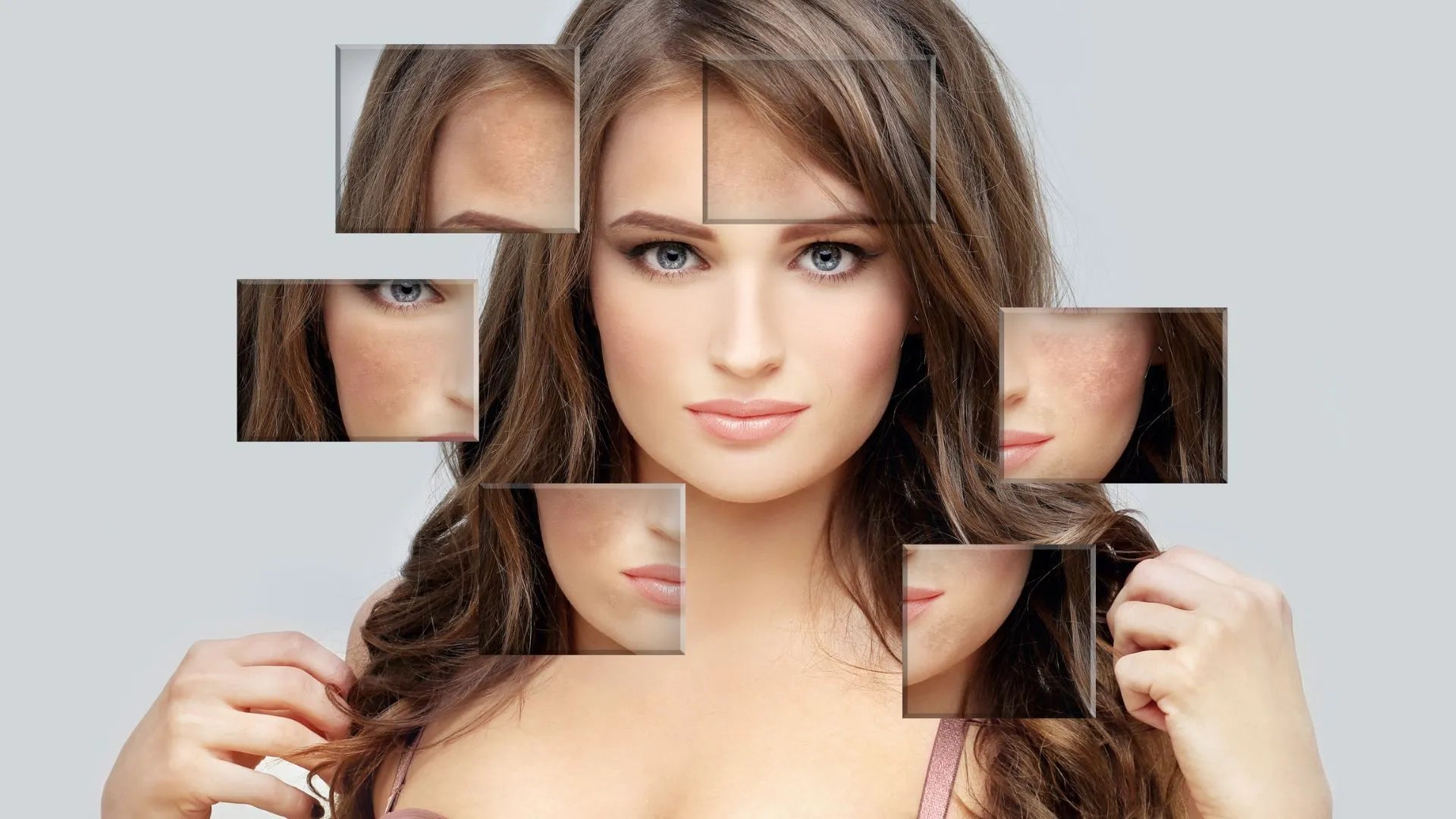
Do you ever wonder why your skin has different shades of color? The answer lies in the process of skin pigmentation. Pigmentation of the skin is due to various factors that influence the production and distribution of melanin, the pigment responsible for the color of your skin.
What Is Skin Pigmentation?
Skin pigmentation refers to the coloration of the skin, which can range from light to dark. It is determined by the amount and type of melanin produced by specialized skin cells called melanocytes. Melanin is a pigment that absorbs ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun, protecting the skin from its harmful effects.
Causes of Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Skin pigmentation disorders can arise from several factors, including:
- Genetics: Some people are genetically predisposed to certain skin pigmentation disorders.
- Environmental factors: Sun exposure, pollution, and certain chemicals can affect skin pigmentation.
- Hormonal changes: Hormonal imbalances during pregnancy or menopause can lead to changes in skin pigmentation.
- Inflammatory conditions: Skin inflammation caused by conditions like acne or eczema can result in hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
- Medications: Certain medications, such as chemotherapy drugs or antibiotics, can cause pigmentation changes.
Types of Skin Pigmentation Disorders
There are various types of skin pigmentation disorders, each with its own characteristics:
- Hyperpigmentation: This condition causes patches of skin to become darker than the surrounding areas. It can be caused by sun exposure, hormonal changes, or inflammation.
- Hypopigmentation: Hypopigmentation refers to areas of skin that are lighter in color than the surrounding skin. It can be caused by conditions like vitiligo or certain fungal infections.
- Depigmentation: Depigmentation occurs when the skin loses its natural pigment, resulting in white patches. It is commonly associated with conditions like vitiligo or albinism.
Diagnosis and Treatment
If you suspect you have a skin pigmentation disorder, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis. They may perform a visual examination, conduct tests, or refer you to a dermatologist.
The treatment of skin pigmentation disorders depends on the specific condition and its underlying cause. Some common treatment options include:
- Topical creams: Prescription creams containing ingredients like hydroquinone or retinoids can help lighten or even out skin tone.
- Cosmetic procedures: Procedures like chemical peels, microdermabrasion, or laser therapy can help improve the appearance of hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation.
- Medications: In certain cases, oral medications or injections may be prescribed to treat underlying causes of pigmentation disorders.
- Sun protection: Protecting your skin from the sun's harmful UV rays is crucial in managing and preventing further pigmentation issues. Always use sunscreen with a high SPF and wear protective clothing when exposed to the sun.
Living With Skin Pigmentation Disorders
Living with a skin pigmentation disorder can have both physical and emotional impacts. It is important to remember that these conditions are common and do not pose a threat to your overall health.
However, if you feel self-conscious or have concerns about your skin pigmentation, consider seeking support from healthcare professionals or support groups who can provide guidance and help you navigate any challenges you may face.
Takeaways
Skin pigmentation is a complex process influenced by genetics, environmental factors, and hormonal changes. Understanding the causes and types of skin pigmentation disorders can empower you to take control of your skin health.
If you suspect you have a skin pigmentation disorder, consult a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment options. Remember to protect your skin from the sun and seek support if needed. Embrace your unique skin, as it is a beautiful reflection of who you are.