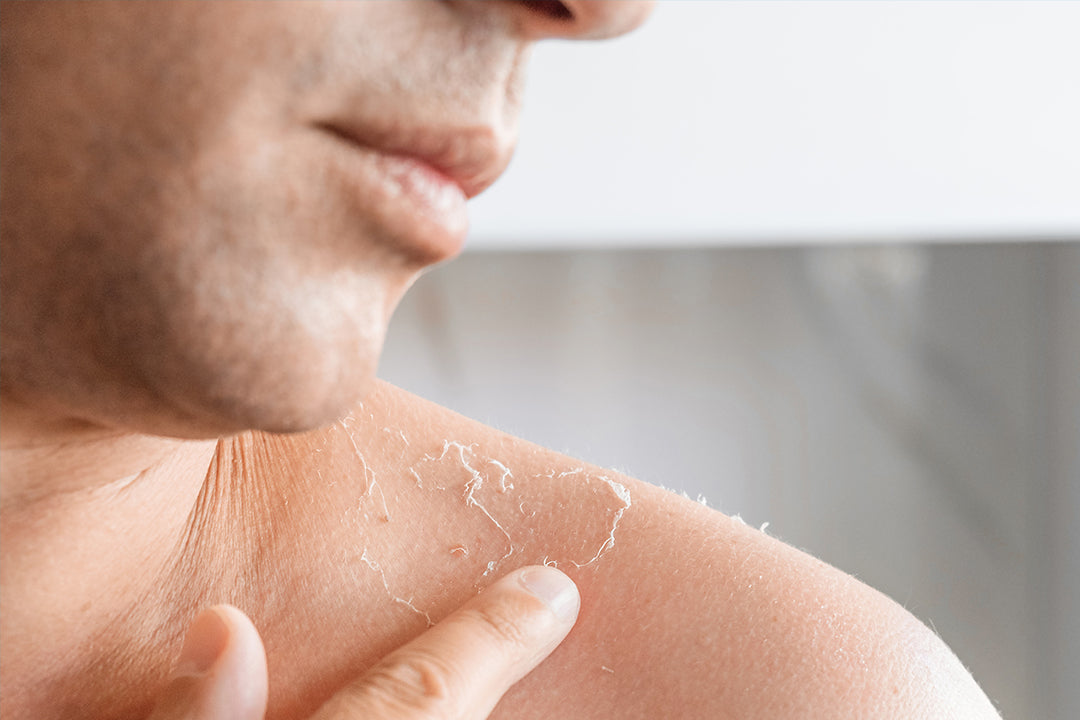
If you suffer from eczema, you know how frustrating and uncomfortable it can be. The constant itching and irritation can greatly impact your quality of life. While there is no cure for eczema, there are ways to manage and reduce flare-ups. One effective approach is adopting an anti-inflammatory diet.
Eczema, also known as atopic dermatitis, is an inflammatory skin condition characterized by dry, itchy, and red patches. The underlying cause of eczema is still not fully understood, but research has shown that inflammation plays a significant role in its development and symptoms.
The Benefits of an Anti-Inflammatory Diet
An anti-inflammatory diet focuses on consuming foods that have natural anti-inflammatory properties. By incorporating these foods into your daily meals, you can help reduce inflammation in your body, including your skin.
Studies have shown that certain foods can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms, while others can help alleviate them. By eliminating or minimizing foods that promote inflammation and incorporating foods that have anti-inflammatory properties, you can potentially reduce the frequency and severity of your eczema flare-ups.
What to Eat
When following an anti-inflammatory diet for itchy skin, it is important to include a variety of nutrient-rich foods. Here are some key foods to incorporate:
- Fatty Fish: Fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines are rich in omega-3 fatty acids, which have anti-inflammatory properties.
- Probiotic Foods: Foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut contain beneficial bacteria that can help support a healthy gut, which is important for reducing inflammation.
- Foods High in Flavonoids: Flavonoids are natural compounds found in fruits and vegetables that have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Berries, citrus fruits, leafy greens, and broccoli are all good sources of flavonoids.
What to Avoid
Just as there are foods that can help reduce inflammation, there are also foods that can trigger or worsen eczema symptoms. Here are some foods to avoid or minimize:
- Ultra-Processed Foods: These foods often contain artificial additives, preservatives, and unhealthy fats, which can promote inflammation in the body.
- Foods High in Sugar: Consuming excessive amounts of sugar can lead to increased inflammation in the body. Limit your intake of sugary drinks, desserts, and processed snacks.
- Refined Carbohydrates: Foods like white bread, pasta, and rice have a high glycemic index, which means they can cause a rapid increase in blood sugar levels and promote inflammation.
Additional Tips for Managing Eczema
In addition to following an anti-inflammatory diet, there are other lifestyle changes and strategies that can help manage eczema:
- Moisturize your skin regularly to prevent dryness and itchiness.
- Avoid known triggers, such as certain fabrics, harsh soaps, and extreme temperatures.
- Manage stress levels, as stress can worsen eczema symptoms.
- Consider using natural remedies, such as oatmeal baths or chamomile tea compresses, to soothe irritated skin.
Takeaways
An anti-inflammatory diet can be a powerful tool in managing eczema symptoms and reducing flare-ups. By incorporating foods that have anti-inflammatory properties and avoiding those that promote inflammation, you can potentially improve your skin's condition and overall well-being. Remember to consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before making any significant changes to your diet.